WordPress custom post types
We now fully support WordPress Custom Post types. For more information, please see our documentation.

Changelog
Stay up to date with all of the latest additions and improvements we've made to Cloudpress.
We now fully support WordPress Custom Post types. For more information, please see our documentation.

Notion code blocks allow you to specify a language for the code inside the code block. Cloudpress now uses the language you set in your Notion code blocks when exporting to the various CMSs. The support level depends on the target CMS, as not all CMSs support code block languages completely. More details are provided in the table below.
| CMS | Level of support |
| Contentful Rich Text | 🚫 Not supported since Contentful Rich Text fields do not support code blocks at all |
| Contentful Long Text (markdown) | ✅ Supported |
| Kentico | 🚫 Not supported |
| Sanity | ✅ Supported. The languages are limited by the ones supported by the Sanity code block. |
| Webflow | ✅ Supported. Cloudpress adds the class hljs language-<language> to the code blocks, so you can enable sytax highlighting by adding Highlight.js to your site. |
| WordPress Gutenberg | 🚫 Not supported. The standard Gutenberg code block does not support code languages. We are investigating supporting 3rd party blocks. |
| WordPress Classic | ✅ Supported. Cloudpress adds the class hljs language-<language> to the code blocks, so you can enable sytax highlighting by adding Highlight.js to your site. |
You have been able to export additional fields from Google Docs to your CMS for a while now. However, for Sanity, this feature has never worked remarkably well. The main reason is that Cloudpress cannot query your Sanity schema, so it does not know the types of your fields. The result was that - more often than not - Cloudpress updated the field in the wrong format.
We have now added the ability to define your additional field types in Cloudpress. When you do this, Cloudpress will update all your fields in the correct format. The video below demonstrates this new feature.
We have expanded our Raw Content Block support to Notion, allowing you to send raw content to your underlying CMS from Notion. We also added documentation on how to use Raw Content Blocks.
The video below demonstrates how you can use Raw Content Blocks to export custom Gutenberg blocks from Notion to WordPress.
You can now use Raw Content Blocks inside Google Docs, allowing you to send raw content to your underlying CMS. This opens up incredible opportunities to export content that Cloudpress cannot handle natively. In WordPress, for example, you can use this feature to export custom Gutenberg blocks like a call-to-action, newsletter signup form, countdown timer, and more.
The video below demonstrates this feature with Google Docs and WordPress.
We now support underline, strike-through, and inline code formatting for Sanity.

You can now map Notion properties to custom fields in WordPress when using our Collection feature.
You can now map Notion pages to existing items in your CMS (i.e. items you created before adopting Cloudpress).
You can specify the image alignment for Webflow images from the Export Settings page of your Webflow connection.

We now support updating custom WordPress fields. For more information on enabling this for your WordPress connection and examples of using it with the most common custom fields WordPress plugins, refer to our updated documentation.

You can now specify reference fields for Webflow by name. The video below demonstrates this feature.
Cloudpress now allows you to add Webhooks for when documents are exported. This is useful when you use Cloudpress in automation tools like Zapier or Make.com, and want automation scripts to run after a document has been exported.

You can now specify the export settings when exporting a Google Doc from the Export Content page in the Cloudpress application.
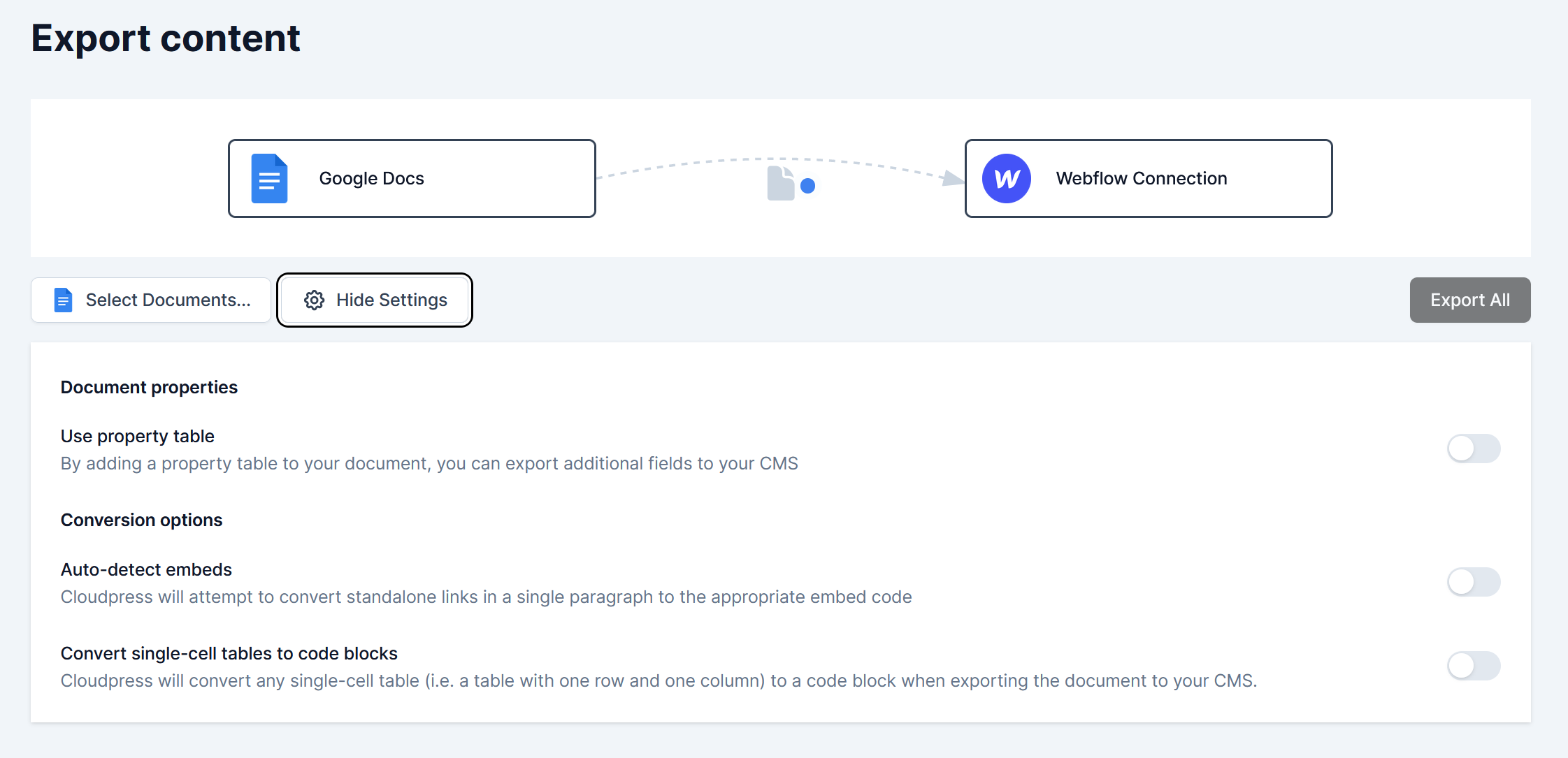 These settings allow you to specify how Cloudpress should process the documents you are exporting:
These settings allow you to specify how Cloudpress should process the documents you are exporting:
Cloudpress now supports footnotes in Google Docs. When adding footnotes to a document, Cloudpress will append the footnotes to the bottom of the content when exporting the document to your CMS.
Let’s take the following Google Doc:
 When exported to WordPress, the footnotes will be rendered as per the screenshot below.
When exported to WordPress, the footnotes will be rendered as per the screenshot below.

With the release of Collection filters yesterday, we have also removed the beta label from Collections. With this, we have now added a full set of documentation for working with Collections in Cloudpress.
Cloudpress now allows you to filter items in a collection. You can read our announcement blog post or watch the video below for more information.
Cloudpress now allows you to update existing content - i.e. content not created with Cloudpress - when exporting documents with the Google Docs Add-on. The video below gives a demonstration of using this feature.
Cloudpress now supports exporting to WordPress pages. You can configure this from the Export Settings tab of your WordPress connection.
 A single connection can only support posts or pages, so you must create two separate connections to export to both.
A single connection can only support posts or pages, so you must create two separate connections to export to both.